之前分享过哈尔滨医科大学李霞老师实验室开发的lncRNA-chromatin相互作用数据库——LnChrom (http://biocc.hrbmu.edu.cn/LnChrom/index.jsp) 。这次详细解读数据库背后所做的分析,同时总结文章的思路、结论和成果以及对其他研究的启发。

文章信息
题目:Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-chromatin interactions reveals lncRNA functions dependent on binding diverse regulatory elements
杂志:Journal of Biological Chemistry
时间:Sept.4, 2019
链接:http://www.jbc.org/content/294/43/15613
主要内容
lncRNA在人类正常生命活动和疾病中扮演者重要的角色,其可以与染色质相互作用,然后招募蛋白质复合物改变染色质状态,进而调控基因表达。然而,lncRNA与染色质相互作用是如何影响并调节生物功能还并不清晰。基于此作者从人类和小鼠数据集中收集了188,647个lncRNA-chromatin相互作用对。他们的结果发现lncRNA在其结合位点展现了不同的表观修饰方式,尤其是在有增强子活动标记的区域。进而对lncRNA的靶基因的功能分析发现lncRNA即可以通过结合启动子调控元件发挥功能,也可以通过结合增强子发挥功能,尤其是在远端调控区域的调控元件。
文章思路
数据资源
| 物种 | 数据类型 | 数据量 |
|---|---|---|
| 人 | ChIRP-,CHOP-CHART-seq | 27 lncRNA-chromatin interaction for 12 lncRNAs |
| ChIP-seq (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, H3K27me3 and H3K36me3) | 52 | |
| DNase-Seq | 8 | |
| 鼠 | ChIRP-,CHOP-CHART-seq | 25 lncRNA-chromatin interaction for 10 lncRNAs |
| ChIP-seq (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, H3K27me3 and H3K36me3) | 42 |
数据来源:
文献收集(ChIRP-,CHOP-,RAP-, CHART-seq)
- Chu, C., et al., Genomic maps of long noncoding RNA occupancy reveal principles of RNA-chromatin interactions. Mol Cell, 2011. 44(4): p. 667-78.
- Simon, M.D., et al., The genomic binding sites of a noncoding RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. 108(51): p. 20497-502.
- Engreitz, J.M., et al., The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome. Science, 2013.341(6147): p. 1237973.
- Mondal, T., et al., MEG3 long noncoding RNA regulates the TGF-beta pathway genes through formation of RNA-DNA triplex structures. Nat Commun, 2015. 6: p. 7743.
数据库
补充知识
ChIRP-seq
与CHART-seq技术类似,都是研究nc-RNA结合的基因组位点,以及作用的蛋白质。
参考:https://www.illumina.com/science/sequencing-method-explorer/kits-and-arrays/chirp-seq.html
ChIRP, also commonly referred to as ChIRP-seq, is a protocol to detect the locations on the genome where ncRNAs, such as lncRNAs, and their proteins are bound. In this method, samples are first crosslinked and sonicated. Biotinylated tiling oligos are hybridized to the RNAs of interest, and the complexes are captured with streptavidin magnetic beads. After treatment with RNase H, the DNA is extracted and sequenced. Deep sequencing can determine the lncRNA/protein interaction site at single-base resolution.
Pros:
- Identifies binding sites anywhere on the genome
- Enables discovery of new binding sites
- Allows selection of specific RNAs of interest
Cons:
- Nonspecific oligonucleotide interactions can lead to misinterpretation of binding sites
- Chromatin can be disrupted during the preparation stage
- The sequence of the RNA of interest must be known
CHART-seq
CHART-seq用于鉴定nc-RNA结合的基因组位点,同时可以鉴定与其作用的蛋白质。
参考Illumina官网:https://www.illumina.com/science/sequencing-method-explorer/kits-and-arrays/chart.html

CHART maps genomic binding sites of ncRNAs by isolating and sequencing the DNA regions where the crosslinked RNA-DNA-protein complexes are bound. CHART differs from other crosslinked-complex purification techniques, such as ChIRP, due to the use of biotinylated 24 nt oligonucleotides (C-oligos) that are highly sensitive and unique to the ncRNA of interest.
An RNase H mapping assay is used to design the 24 nt sequence of the C-oligos. First, nuclei samples are crosslinked and fragmented. Next, C-oligos are hybridized to the complex and bound to streptavidin beads. The mixture is washed and the complex eluted. The DNA is isolated and sequenced, and the proteins involved in the complex are isolated and analyzed by Western blots.
Pros:
- Maps genomic binding sites of lncRNAs
- Simultaneously identify proteins associated with the lncRNA complex
Cons:
- Needs large amount of nuclei (1x109 cells)
- RAP-seq
RAP isolates lncRNAs and maps the sequence of their target DNA through a probe-capture mechanism. First, the cells are crosslinked and lysed before DNase I chromatin digestion to 100–300 bp DNA fragments. Biotinylated RNA probes, antisense to the lncRNA, are hybridized and captured with streptavidin. The biotin-RNA probes are 120 nt and are tiled every 15 nt over the span of the lncRNA. The captured complexes are eluted and prepared for sequencing. RNA library preparation is done through RAP-RNA, and DNA library preparation by standard chromatin immuniprecipitation (ChIP).
Pros:
- Genomic mapping of lncRNA targets
- Possible to sequence RNA and DNA from the purification products
- Long RNA probe length provides high binding affinity to the target lncRNA1
- Minimal amplification steps during RNA sequencing after purification of the lncRNA complex
Cons:
- Requires RNA sequence to be known
- ChOP-seq
Detection of RNA–DNA binding sites in long noncoding RNAs
鉴定lncRNA结合位点
方法
方法参考文献:West, J.A., et al., The long noncoding RNAs NEAT1 and MALAT1 bind active chromatin sites. Mol Cell, 2014. 55(5): p. 791-802.
文章中认为lncRNA的结合位点即lncRNA-chromatin interaction对个数,方法是参考以上文献,该文献利用CHART-seq技术鉴定lncRNA结合位点以及相互作用的蛋白质。
结果
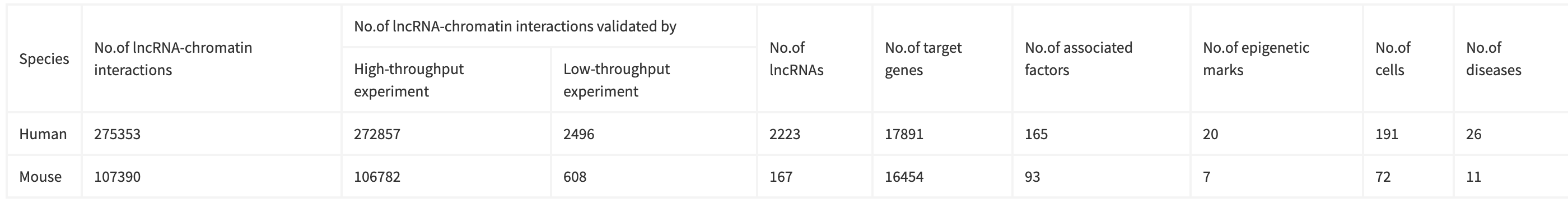
去除掉缺少“even”和“odd”样本的lncRNA、低富集度和在GENCODE v27中缺乏注释的lncRNA,最终在人类和鼠中分别鉴定到77,031和111,616个lncRNA-chromatin interaction(lncRNA-chromatin interaction可以理解为lncRNA结合位点)。
每个结合位点的大小平均小于1kb,除了SRA (在2kb左右) (图B)。
下图A展示的是人中的lncRNA-chromatin interaction, 横坐标包含l ncRNA和细胞系,图中展示的是11个lncRNA,其中一个lncRNA应该是由于缺少“even”和“odd”样本被过滤了
结合位点的基因组分布特征
- 方法
基因组分布特征即在启动子、远端等区域的结合,Homer软件注释可以得到该结果,ChIPseeker也可以做类似的分析。
- 结果
大多lncRNA的结合位点位于其最邻近基因的转录起始位点(TSS)的远端(Distal)区域。该结论在多个研究中都有提及,lncRNA大部分是位于其转录位点的远端区域,与蛋白质相互作用的方式通常是反式作用。
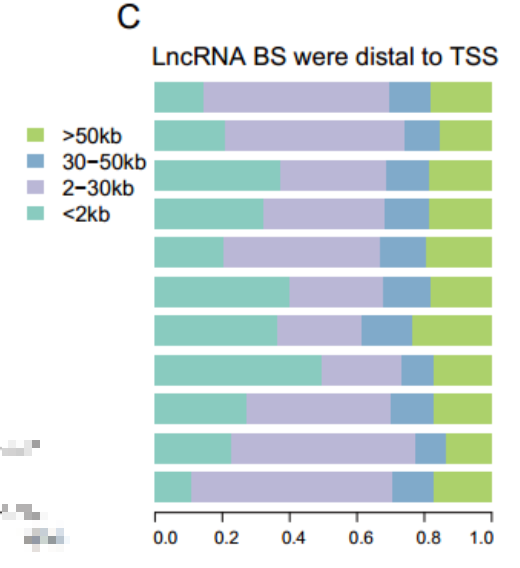
lnCRANs结合位点的保守性
方法
保守性评估采用的是2005年发表的方法——phastCons,这篇文章至今已有3000+的引用,该模型是基于一个二态系统发育隐马尔可夫模型(phylo HMM),phastCons通过最大似然法拟合一个phylo HMM的数值,跨物种校准模型,然后基于该模型预测保守元件
文献:doi: 10.1101/gr.3715005 ; PMID: 16024819
Evolutionarily conserved elements in vertebrate, insect, worm, and yeast genomes.
结果
他们发现人类的lncRNAs结合位点与DHSs(DNase I hypersensitive sites)相比有更高的保守性。
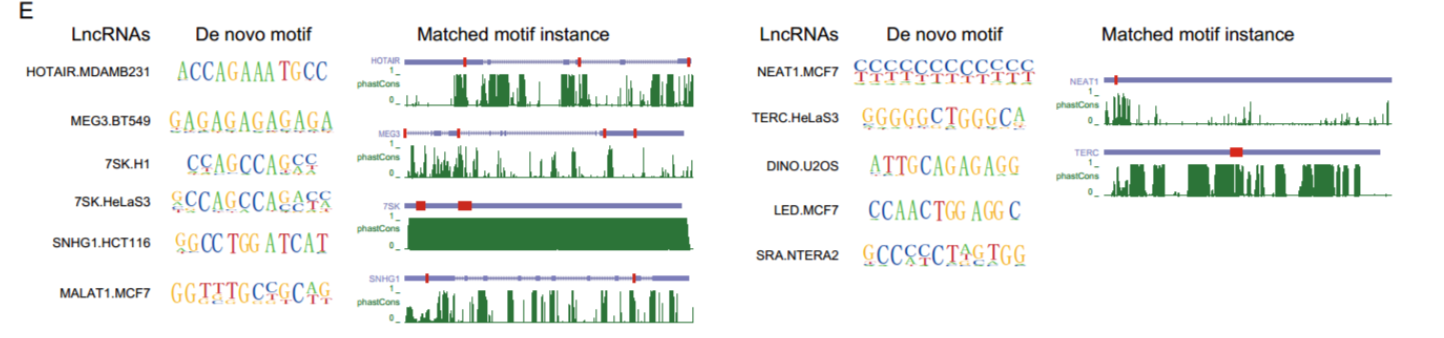
lnCRANs结合位点的motif分析
方法
HOMER
结果
de novo DNA-binding motifs的结果与之前的发现一致,如HOTAIR 和 MEG3结合位点富集在GA嘌呤处。而且发现有些motif可以与lncRNA的序列匹配,表明这些lncRNA可能形成DNA:RNA三螺旋结构。
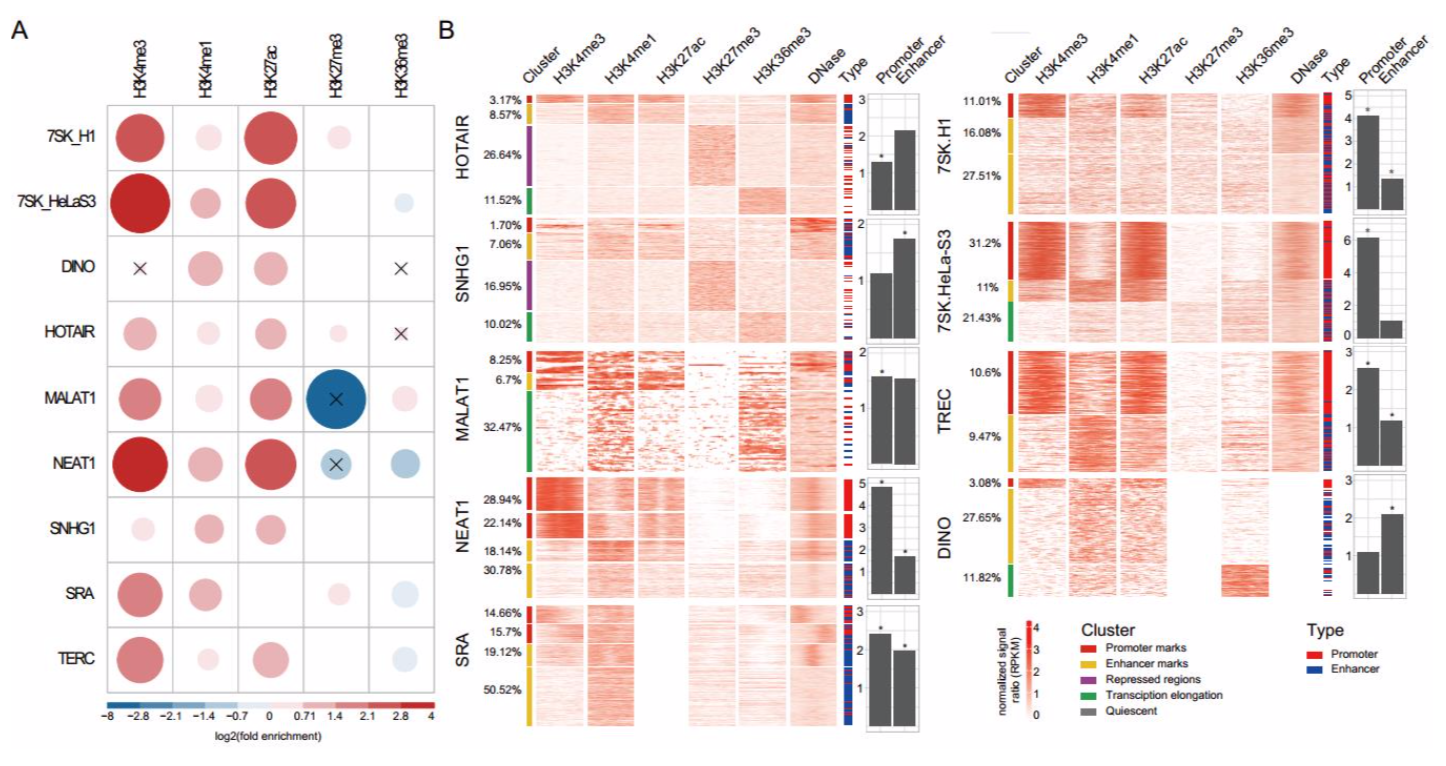
lncRNA结合位点与表观修饰的关联
方法
genome association tool (GAT) : 该方法是评估两个基因组片段的相关性,如ChIP-seq和RNA-seq的重合的区域是否显著相关。
Motivation: A common question in genomic analysis is whether two sets of genomic intervals overlap significantly. This question arises, for example, when interpreting ChIP-Seq or RNA-Seq data in functional terms. Because genome organization is complex, answering this question is non-trivial.
Summary: We present Genomic Association Test (GAT), a tool for estimating the significance of overlap between multiple sets of genomic intervals. GAT implements a null model that the two sets of intervals are placed independently of one another, but allows each set’s density to depend on external variables, for example, isochore structure or chromosome identity. GAT estimates statistical significance based on simulation and controls for multiple tests using the false discovery rate.
Availability: GAT’s source code, documentation and tutorials are available at http://code.google.com/p/genomic-association-tester.
选择了5种组蛋白修饰数据类型:H3K4me3, H3K4me1,H3K27me3, H3K36me3, H3K27ac
promotor: high H3K4me3
enchancer: high H3K4me1and low H3K4me3
- repressed: H3K27me3
- transcription elongation : high H3K36me3
- quiescent: low H3K36me3
- 结果
只有lncRNA的数据同时包含相对应的细胞系至少两个表观修饰数据的lncRNA最后被保留用于这部分的分析。人类和鼠分别是9个和8个lncRNA。lncRNA结合位点与染色质修饰的关联多种多样,所有的lncRNA在H3K4me1 和 H3K27ac mark区域显著富集。
为了进一步探究lncRNA结合位点的表观修饰模式,作者观察了lncRNA结合位点2kb以内的染色质可及性。发现lncRNA在其结合位点展现不同的表观修饰模式,如可以结合在启动子、增强子、抑制子等。
lncRNA结合区域与其潜在的靶基因
方法
如果一个基因的TSS上下游1kb与lncRNA结合位点区域重合,就定义为该基因为此lncRNA的promoter 靶基因;
当lncRNA结合位点与远端(distal)调控元件作用(>2kb to nearest TSSs)时,同时结合 来自4D genome database 的long-range 染色质相互作用数据,鉴定到lncRNA的distal 靶基因
结果
不同的lncRNA靶基因数目差异很大,平均每个lncRNA的蛋白编码靶基因为3100个。其中LncRNA 7SK有8051个蛋白编码靶基因(最多)。同时,他们观察到一些lncRNA的promoter和distal 靶基因有显著的重合,表明lncRNA与启动子和远端调控元件结合靶向于相同的基因。
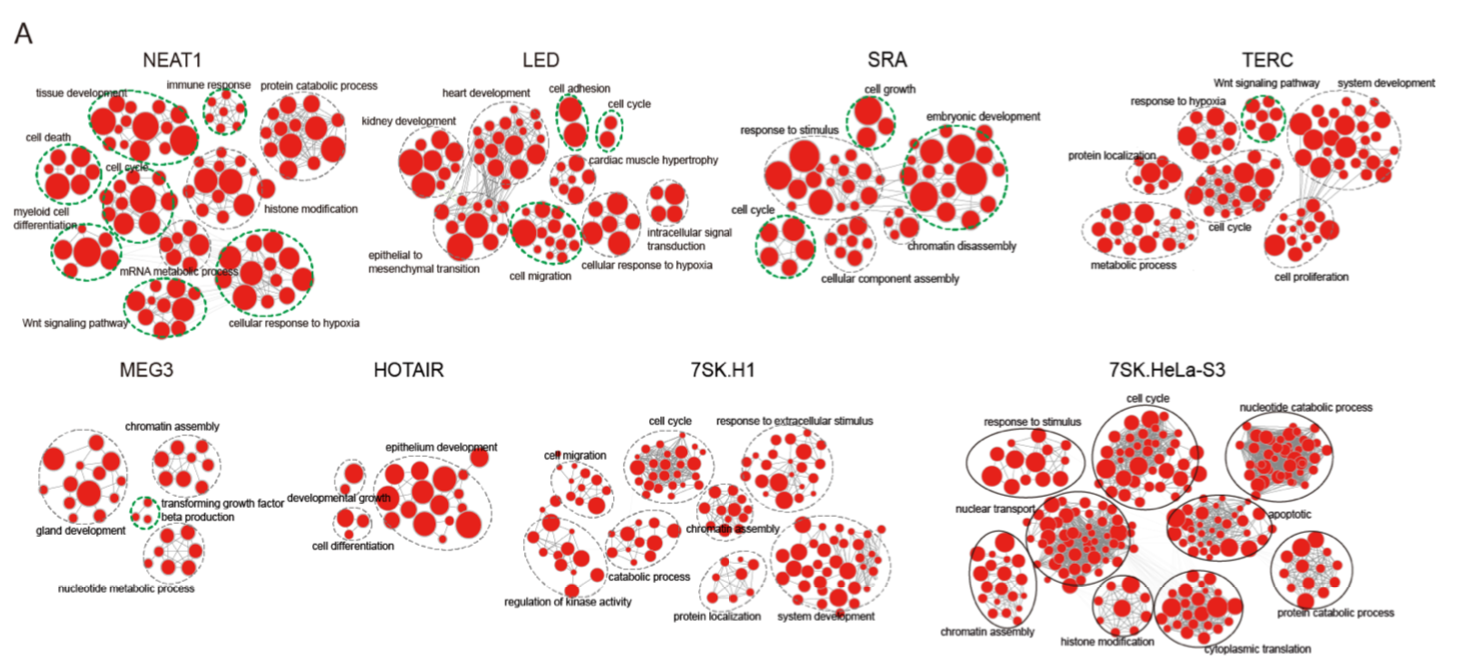
lncRNA结合区域与其潜在的靶基因的功能
方法
对每个lncRNA的靶基因进行GO/KEGG功能注释
clusterProfiler
结果
功能注释结果发现这些lncRNA都能富集到其已知的功能,如cancer-related lncRNA NEAT1 富集到细胞分化、细胞周期和细胞死亡。
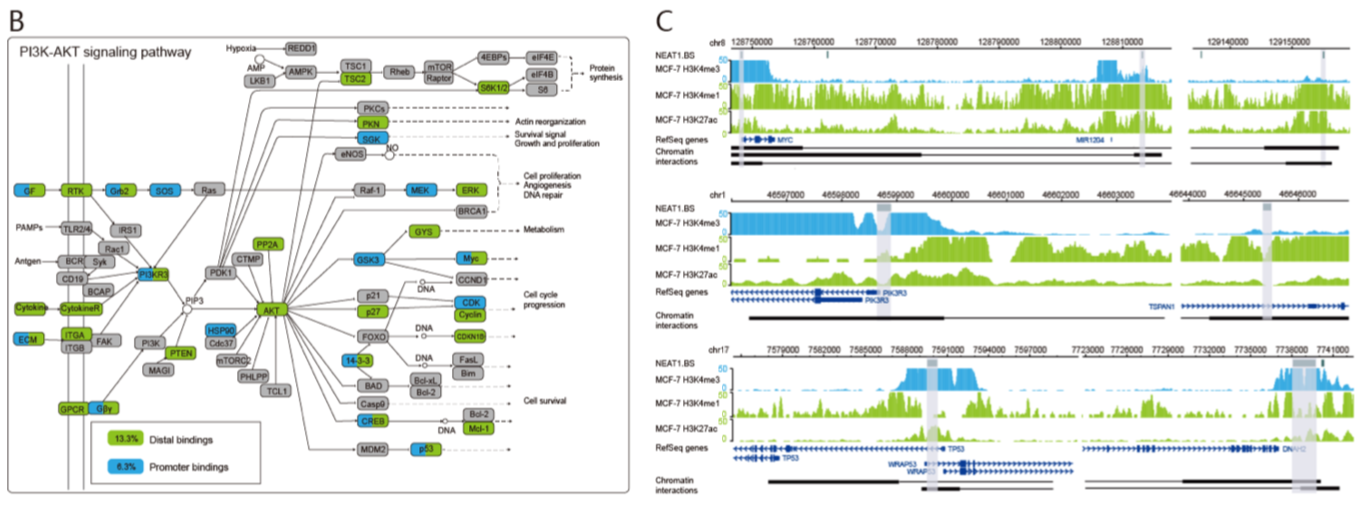
为了进一步确定lncRNA是如何参与通路的调控,他们将lncRNA的靶基因与富集通路匹配对应。发现lncRNA既可以结合启动子调控元件发挥功能,也可以结合远端调控元件发挥功能。
lncRNA-target genes在人类肿瘤预后诊断中的应用
方法
生存分析: Kaplan-Meier method
结果
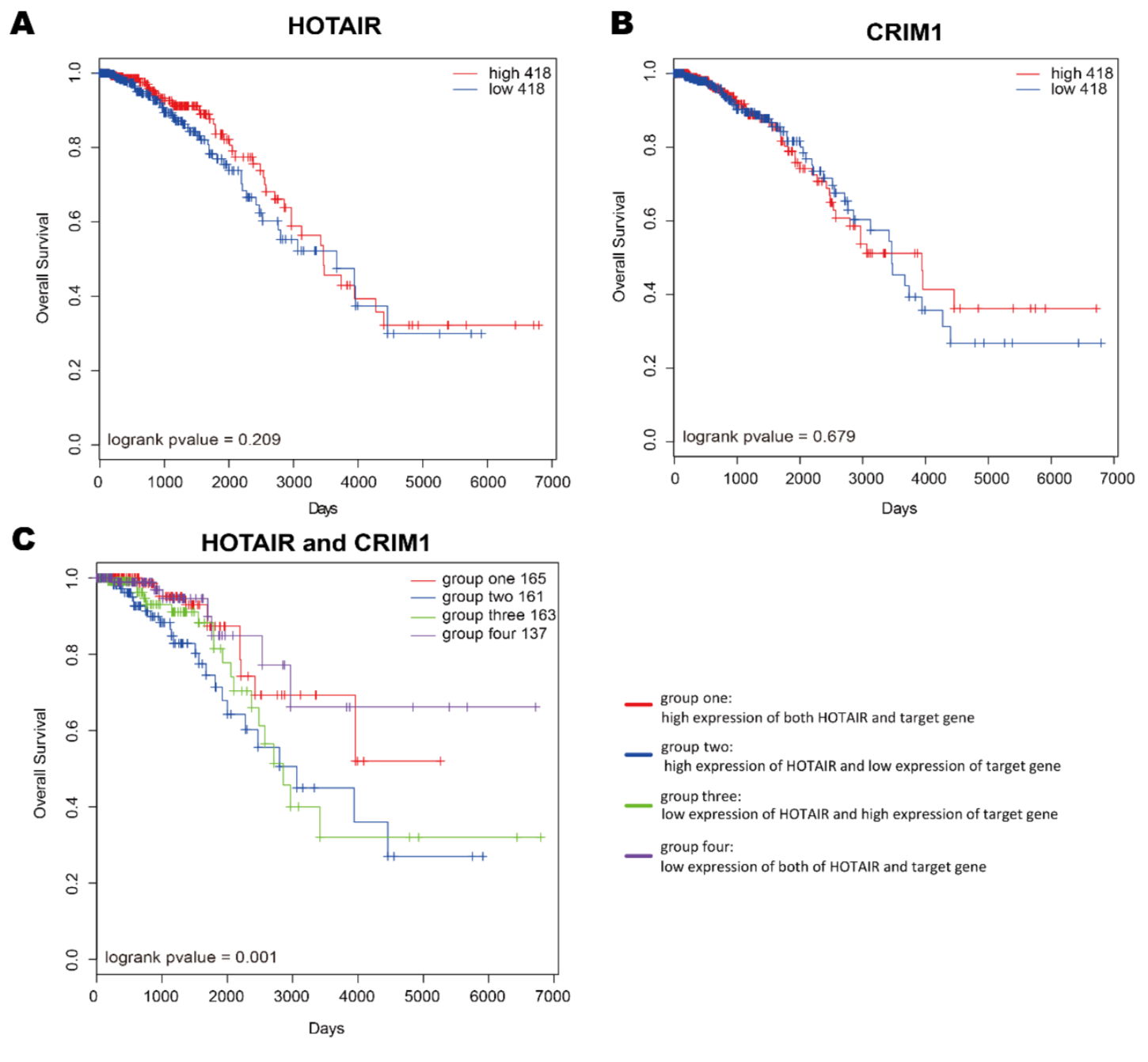
从TCGA中收集了3肿瘤类型1330个癌症病人的基因表达数据(包括蛋白编码和lncRNA),根据lncRNA表达的中位数,将病人分为high-risk group和low-risk group.