文章信息
题目:Deep learning improves antimicrobial peptide recognition
杂志:Bioinformatics
IF: 5.610 (2019)
时间:24 march, 2018
链接:doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty179
一句话评价
通过卷积网络层和循环神经网络层组合构建的深度学习模型识别抗生肽。
文章介绍
概述
- 细菌对抗生素药物的抗性越来越引起人们的关注,对经济,生命健康和社会造成重要的挑战。抗生肽(Antimicrobial peptides ,AMPs)是天然免疫的组成部分,也是研发药物广泛使用的靶点。机器学习的方法可以为湿实验的研究者提供一些潜在的研究位点。
- 这篇文章使用卷积网络层和循环神经网络层组成的神经网络模型识别抗菌活动。最终训练的模型也比一般的方法表现更好。此外,通过潜入权重(Embedding Weights),他们提出了reduced-alphabet representation的方法,最终实现可以只用9个氨基酸分子准确识别AMP。
- 最后,他们也提供了模型和数据相关的网站:Antimicrobial Peptide Scanner vr.2 web server, www.ampscanner.com
方法
数据
- APD vr.3 database: http://aps.unmc.edu/AP, 主要是革兰氏阴性和阳性细菌的AMP
- 过滤掉长度小于10的氨基酸以及和CD-Hit > 90%的共有的序列,最终使用的AMP有1778个,训练集:712,验证集:354,测试集:712。
- 人工构建了non-AMP的序列:Torrent et al., 2011; Xiao et al., 2013
- Torrent,M. et al. (2011) Connecting peptide physicochemical and antimicro- bial properties by a rational prediction model. PLoS One, 6, e16968.
- Xiao,X. et al. (2013) iAMP-2L: a two-level multi-label classifier for identifying antimicrobial peptides and their functional types. Anal. Biochem., 436, 168–177.
- 从UniProt下载了肽段序列,并过滤掉包含抗性的序列
模型
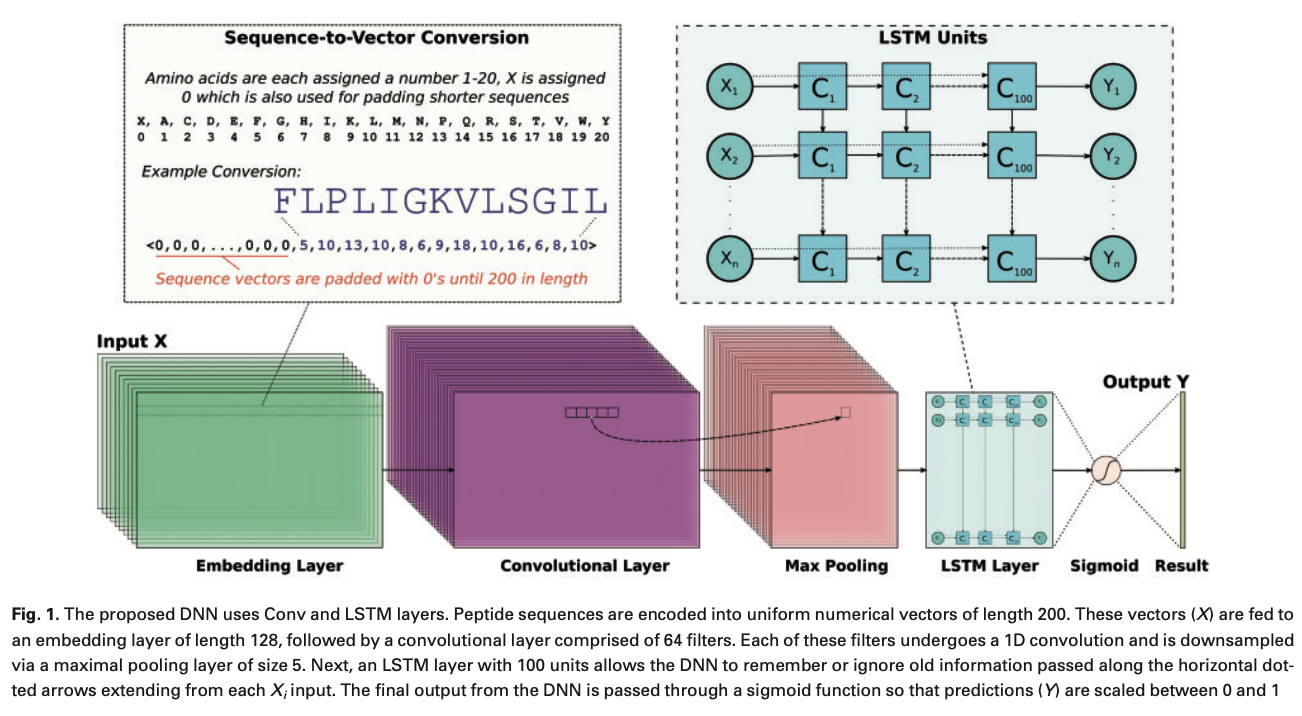
基于Keras框架搭建的模型:
- 肽段序列被编码为长度为200的序列,20个氨基酸依次编码为1-20,其余以0填充。
- embedding_vector_length: 128
- 卷积层:1D convolution,
nb_filter: 64, filter_length: 16, init: normal, strides: 1, border_mode: same, activation: relu - 池化层:Maxpooling layer,size=5
- LSTM层:100 units,
(unroll: True, stateful: False, dropout: 0.1 and rest default settings) - Dense 层:激活函数:sigmoid
- 其他参数:10 epochs, ‘adam’ 优化器, loss: binary_cros- sentropy, metrics: accuracy).
调参:
Hyperas wrapper package for Keras:https://github.com/maxpumperla/hyperas
模型评估:
用到评估metrics有:
sensitivity (SENS)
specificity (SPEC)
ACC
Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC)
ROC curve: pROC package in R
结果和结论
构建的模型性能:
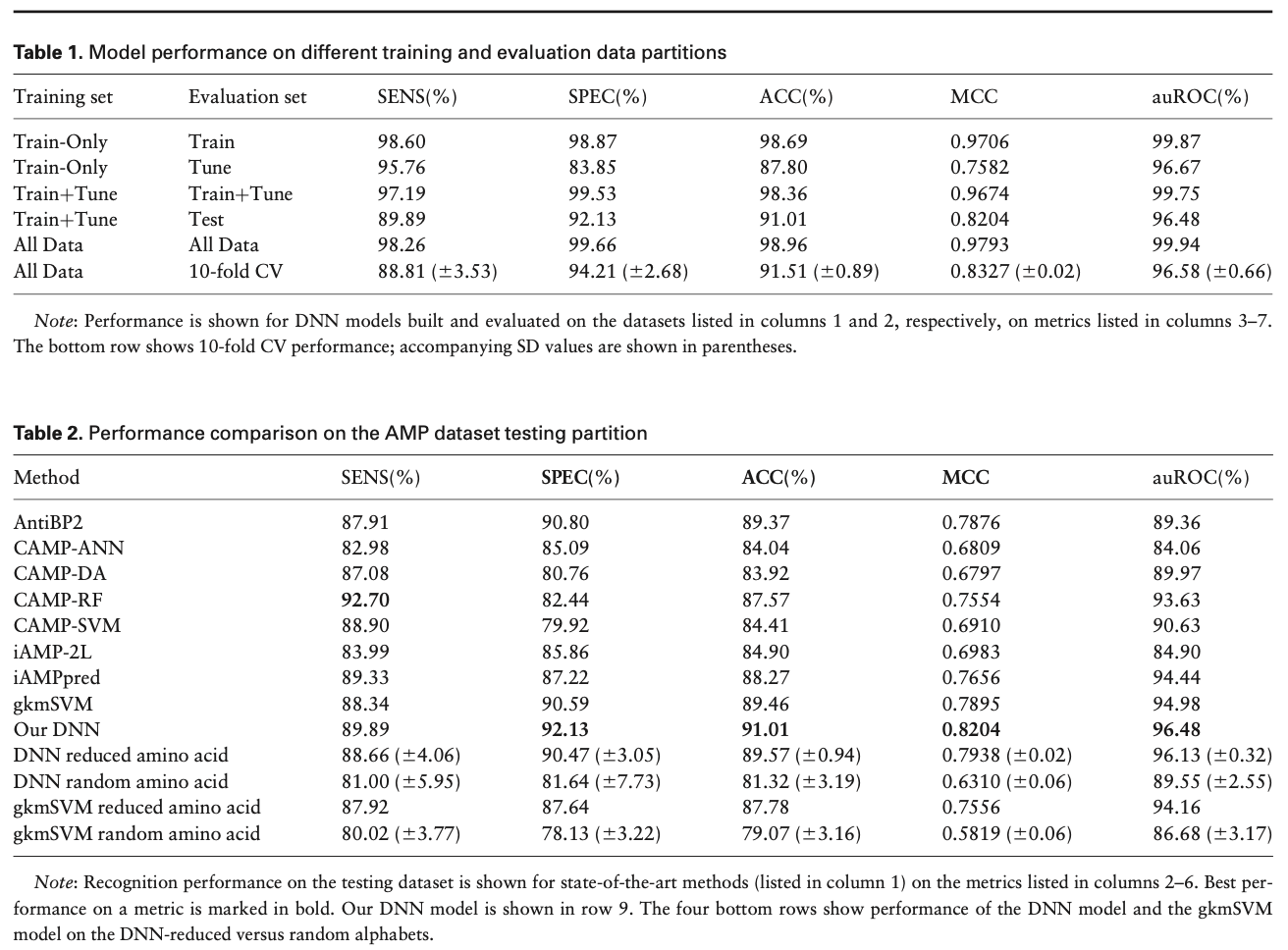
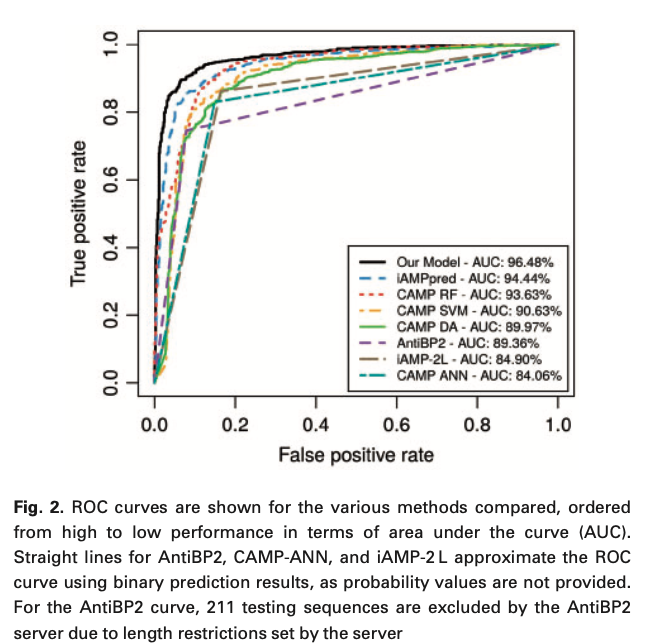
与其他方法的比较
创新性和意义
- 基于抗生肽识别抗菌性活动
- 模型的结构:结合了卷积层和循环神经网络层
- 输入数据的处理:embeding layer的处理
- Reduced alphabet model analysis